acetabular labral tear special tests accuracy|acetabular labral tear imaging : company We investigated the diagnostic validity of clinical tests . Background and purpose An acetabular labral tear is a diagnostic challenge. Various clinical tests have been described, but little is known about their diagnostic sensitivity and specificity. State regulations are updated quarterly; we currently have two versions available. Below is a comparison between our most recent version and the prior quarterly release. More comparison .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Made from Dow Corning Silastic, this tubing is made from the same platinum-cure material that has been implanted in laboratory animals for years. You can sterilize this tubing with EtO gas .
Magnetic resonance arthrography as a diagnostic test for acetabular labral tears has been shown to demonstrate 66%-71% sensitivity and 44%-75% specificity. The accuracy of intra-articular injection of anesthetic to determine an intra-articular abnormality has been found to be 90% [4] .
We investigated the diagnostic validity of clinical tests . Background and purpose An .
acetabular labral test results
acetabular labral test positive
Magnetic resonance arthrography as a diagnostic test for acetabular labral tears has been shown to demonstrate 66%-71% sensitivity and 44%-75% specificity. The accuracy of intra-articular injection of anesthetic to determine an intra-articular abnormality has been found to be 90% [4] .We investigated the diagnostic validity of clinical tests . Background and purpose An acetabular labral tear is a diagnostic challenge. Various clinical tests have been described, but little is known about their diagnostic sensitivity and specificity. While the physical examination has been found to be up to 98% accurate in determining the existence of general intra-articular pathology, identification of specific pathology, like a labral tear, is far less accurate and often needs to be paired with other diagnostic modalities [33, 34, 38, 39, 41]. Often, years may pass before an acetabular . All labral tears were confirmed by arthroscopy, demonstrating that the impingement test is extremely accurate in the diagnosis of labral tears. The McCarthy test for acetabular labral tears 7 was developed earlier than the FADER and FABER tests.
Arthroscopy remains the reference standard for diagnosing acetabular labral tears allowing for dynamic examination and assessing the extent of the tear [50, 52]. However, it is more invasive and may have limited access to posterior labral tears depending on portal positioning [52].A PT, an OS, and two ORs independently performed history and examinations with the emphasis of diagnosis on the results of six special tests. Results: Thirty-two of 37 individuals (86%) had labral tears to the hip at arthroscopy. The injection of an intra-articular contrast medium (gadolinium) and specific sequences increase the accuracy of NMR for chondrolabral lesions, and assist in ruling out synovial diseases. The sequences are usually performed in three planes: coronal, sagittal, and oblique axial (at the femoral-neck plane). Information regarding acetabular labral tears and their association to capsular laxity, femoral acetabular impingement (FAI), dysplasia of the acetabulum, and chondral lesions is emerging.
For MRI (eight studies), the pooled sensitivity for detecting acetabular labral tears was 66% (95% CI 59 to 73) and pooled specificity was 79% (95% CI 67 to 91). For MRA (15 studies), the pooled sensitivity was 87% (95% CI 84 to 90) and pooled specificity was 64% (95% CI 54 to 74). Specific provocative tests for acetabular labral tears have been described in the literature, all of which involve stressing or loading the hip joint in rotation. However, no single test has been identified as having a significant positive predictive value in .Magnetic resonance arthrography as a diagnostic test for acetabular labral tears has been shown to demonstrate 66%-71% sensitivity and 44%-75% specificity. The accuracy of intra-articular injection of anesthetic to determine an intra-articular abnormality has been found to be 90% [4] .
We investigated the diagnostic validity of clinical tests . Background and purpose An acetabular labral tear is a diagnostic challenge. Various clinical tests have been described, but little is known about their diagnostic sensitivity and specificity. While the physical examination has been found to be up to 98% accurate in determining the existence of general intra-articular pathology, identification of specific pathology, like a labral tear, is far less accurate and often needs to be paired with other diagnostic modalities [33, 34, 38, 39, 41]. Often, years may pass before an acetabular . All labral tears were confirmed by arthroscopy, demonstrating that the impingement test is extremely accurate in the diagnosis of labral tears. The McCarthy test for acetabular labral tears 7 was developed earlier than the FADER and FABER tests.
Arthroscopy remains the reference standard for diagnosing acetabular labral tears allowing for dynamic examination and assessing the extent of the tear [50, 52]. However, it is more invasive and may have limited access to posterior labral tears depending on portal positioning [52].A PT, an OS, and two ORs independently performed history and examinations with the emphasis of diagnosis on the results of six special tests. Results: Thirty-two of 37 individuals (86%) had labral tears to the hip at arthroscopy. The injection of an intra-articular contrast medium (gadolinium) and specific sequences increase the accuracy of NMR for chondrolabral lesions, and assist in ruling out synovial diseases. The sequences are usually performed in three planes: coronal, sagittal, and oblique axial (at the femoral-neck plane). Information regarding acetabular labral tears and their association to capsular laxity, femoral acetabular impingement (FAI), dysplasia of the acetabulum, and chondral lesions is emerging.
acetabular labral tears impingement test
For MRI (eight studies), the pooled sensitivity for detecting acetabular labral tears was 66% (95% CI 59 to 73) and pooled specificity was 79% (95% CI 67 to 91). For MRA (15 studies), the pooled sensitivity was 87% (95% CI 84 to 90) and pooled specificity was 64% (95% CI 54 to 74).
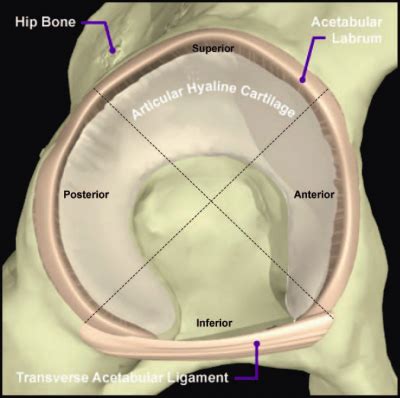

acetabular labral tear test
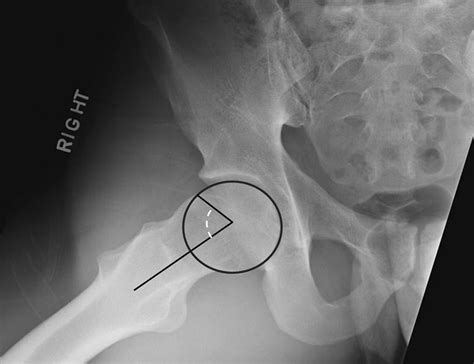
acetabular labral tear prognosis
acetabular labral tear management
acetabular labral tear imaging
SINOMAC glass autoclave is suitable for manufacturing various laminated glass, especially .
acetabular labral tear special tests accuracy|acetabular labral tear imaging